News
1. Meta
Purple Llama is launching open-sourced tools, evaluations, and models to enable the safe and responsible development of AI systems, with offerings such as cybersecurity assessments, attack prevention models, and compliance testing. This initiative aims to democratize access to essential AI security resources (Meta).
Meta introduces Imagine, a separate website housing an text-to-image tool powered by generative AI (FB).
2. Grok, a new ChatGPT competitor
Grok is now available for Premium Plus subscribers in the U.S. Unlike ChatGPT, Grok can integrate real-time data from X into responses (Search Engine Land).
3. Google’s Gemini
Google has released an AI model named Gemini, which boasts advanced “reasoning capabilities” and is designed to “think more carefully” when answering complex questions. Gemini is a foundational model that will be integrated into Google’s existing tools, including search and Bard, and can recognize and generate text, images, and audio (BBC).
4. Microsoft Copilot
Microsoft is updating its Copilot service with new features, including support for OpenAI’s latest GPT-4 Turbo model and an improved DALL-E 3 model. These updates will enhance Copilot’s ability to understand queries with a larger context window and create higher quality, more accurate images, along with introducing a new code interpreter feature for more accurate calculations and data analysis, and a “Deep Search” functionality in Bing (The Verge).
5. Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI has released its own LLMs, pplx-7b-online and pplx-70b-online. These models, fine-tuned versions of open-source models, aim to provide helpful, factual, and up-to-date information, integrating web search data without a knowledge cutoff, potentially making them more current and accurate than existing models like GPT-4 (VentureBeat).
6. Organ aging signatures in the plasma proteome
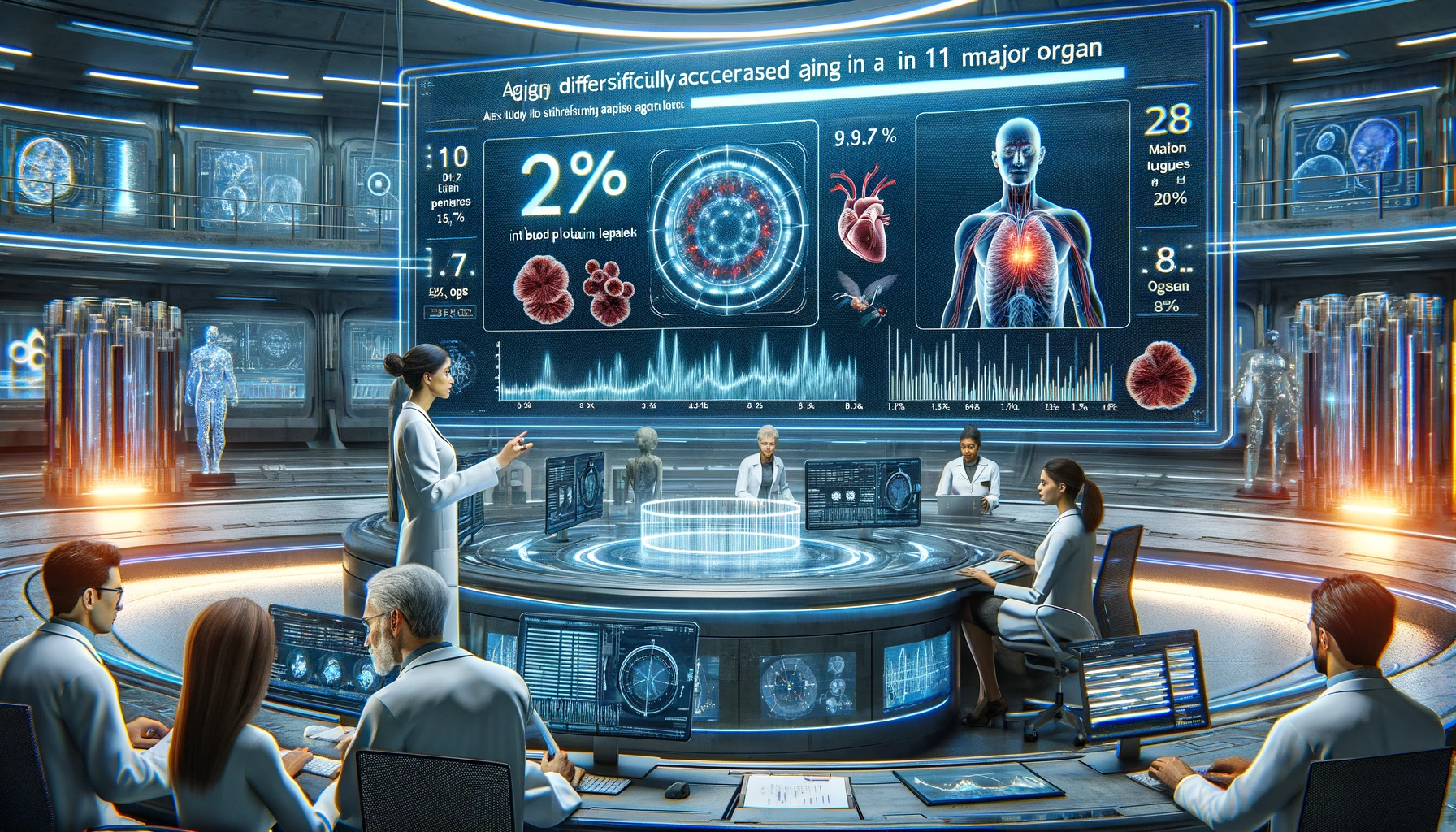
In a study involving human participants, researchers used blood plasma protein levels to assess aging differences in 11 major organs, discovering that nearly 20% of individuals exhibit significantly accelerated aging in one organ, and 1.7% experience accelerated aging in multiple organs. This accelerated organ aging is linked to a higher mortality risk and specific age-related diseases, with findings indicating that individuals with faster aging in certain organs, such as the heart or brain, have a significantly increased risk of related diseases like heart failure or Alzheimer’s (Nature).
7. Single molecules as qubits
Physicists have made a significant advancement towards building quantum computers using individual molecules trapped with optical tweezers, a technique involving highly focused laser beams. Two separate teams have successfully entangled pairs of calcium monofluoride molecules, a key requirement for quantum computing, potentially opening new avenues for processing quantum information and simulating complex materials or fundamental physics forces (Nature).
Articles
1. Medical microrobots that can travel inside your body are (still) on their way (MIT Tech Review)
Medical microrobots, still in development, promise to revolutionize healthcare by performing tasks like breaking up clots, delivering drugs to tumors, and aiding in embryo implantation. These tiny robots, ranging from a micron to a few millimeters in size, are being developed to navigate the human body’s complex environments, with some already tested in large animals and others in phase 1 trials, like Bionaut’s device for treating brain tumors and Dandy-Walker syndrome.
2. CRISPR 2.0: a new wave of gene editors heads for clinical trials (Nature)
Researchers are moving beyond the first generation of CRISPR-Cas9 genome-editing therapies, exploring more versatile CRISPR-based systems that offer greater precision and flexibility. These advanced techniques include base editing, prime editing, and epigenome editing, which can make more specific changes like switching on genes, and are being developed for a range of diseases, including cystic fibrosis and genetic blood disorders.