AI Innovations
1. Command R+
Cohere has introduced Command R+, an advanced large language model (LLM) aimed at enterprise applications, offering significant improvements in multilingual support, retrieval augmented generation (RAG), and scalability over its predecessor. This new model is optimized for enterprise needs, providing enhanced RAG with citations, support for multiple business languages, and a Tool Use API for automating complex workflows, positioning it ahead of competitors in key AI benchmarks (VentureBeat).
Implications: Firms might take advantage of Command R+ for large scale integration of GenAI capabilities.
2. DALL-E
OpenAI has enhanced DALL-E, integrating image editing capabilities directly into the ChatGPT platform, allowing users to modify their AI-generated images without leaving the chat environment. Additionally, DALL-E now offers preset style suggestions to assist users in sparking creativity for image generation, alongside efforts to enhance trust in AI-created images through visible watermarks and metadata (The Verge).
Implications: DALL-E might become more useful for corporations in producing desired images and variations.
3. Stability Audio 2.0
Stability AI has released Stable Audio 2.0, an upgrade that extends the AI’s text-to-music generation capabilities to three minutes, enhancing user options with audio-to-audio transformations and expanded sound-effect generation (Mashable).
Implications: Producing commercial music might become a lot easier, with natural language prompting.
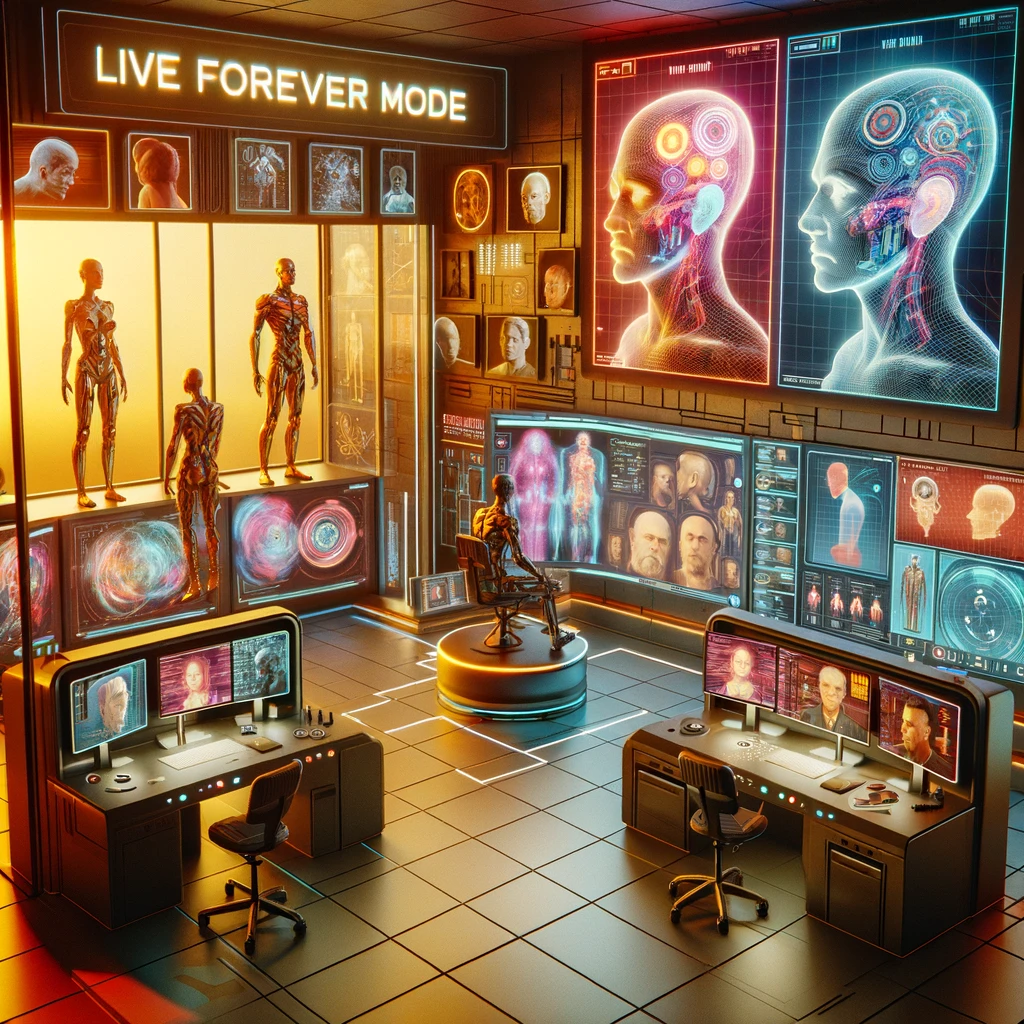
4. Live forever
Artur Sychov and Somnium Space have developed a virtual reality tool named “live forever mode,” which creates digital avatars capable of mimicking a person’s voice, mannerisms, and movements, designed to preserve the essence of individuals for future interaction with loved ones. While this innovative technology offers a novel way to remember and interact with the deceased, it also raises ethical concerns about the commercial exploitation of people’s fear of mortality and the implications of digital immortality (The Mirror).
Implications: Bringing the deceased, the famous, or anything inaccessible to virtual reality may become a trend.
5. Stargate
Microsoft and OpenAI are reportedly collaborating on a $100 billion data center in the U.S., aiming to construct an AI supercomputer named Stargate, which is expected to significantly exceed Microsoft’s previous capital expenditures in the sector. The ambitious project, potentially leveraging nuclear power to meet its substantial energy needs, underscores the growing scale and complexity of AI infrastructure, necessitating careful consideration of environmental impacts and the call for more comprehensive policy frameworks on AI risks (Forbes).
Implications: The bottleneck of computing power in AI might be removed in the future, for some at least.
6. Flood prediction
AI-based forecasting now offers reliable predictions of extreme riverine events in ungauged watersheds, providing timely flood warnings with up to a five-day lead time, surpassing or matching the accuracy of current global systems like the Copernicus Emergency Management Service. This AI model, already operational in over 80 countries, underscores the potential for AI to enhance flood risk mitigation, especially in regions with limited hydrological data, and emphasizes the need for expanded hydrological data availability to refine global flood warning accessibility (Nature).
Implications: Weather forecast will continue to improve with the advancement of AI. This might help us deal with climate change.
7. Local LLM
Opera has introduced a feature allowing users to download and run large language models (LLMs) locally through their browser, starting with Opera One users who receive developer updates. This innovation, which utilizes the Ollama open-source framework, supports over 150 models from various families, including Llama and Gemma, enabling users to interact with AI directly on their devices. While this feature offers access to a broad range of LLMs, Opera advises users to monitor their system’s storage, as each model requires over 2GB of space (TechCrunch).
Implications: Future computers will need larger storage but run LLM locally.
Other Innovations
1. Apple
Apple is reportedly shifting its focus from autonomous cars to developing personal home robots, as indicated by a Bloomberg report, which may include a mobile bot and an advanced robotic table-top display. These projects are in the early stages, with their future uncertain, but they represent a new direction for Apple in integrating artificial intelligence into household devices (CNET).
2. Quantum computing
Microsoft and Quantinuum have announced a significant advancement in quantum computing, enhancing the reliability of quantum computers by using an error-correction algorithm that effectively converts 30 physical qubits into four stable qubits. This breakthrough, which is a stride towards commercializing quantum computing, demonstrates a level of precision and efficiency in qubit stability not previously achieved (Reuters).
3. Rejuvenate immune system
The aging immune system experiences a shift from balanced hematopoietic stem cells (bal-HSCs) that support lymphoid and myeloid cell production to myeloid-biased HSCs (my-HSCs), leading to decreased adaptive immunity and increased inflammation. This imbalance contributes to age-related declines in immune function, as my-HSCs become predominant, reducing lymphopoiesis and enhancing myelopoiesis. Recent research shows that depleting my-HSCs in aged mice can restore aspects of a youthful immune system, improving both primary and secondary responses to viral infections, suggesting a potential strategy for addressing age-related immune system decline (Nature).
4. Energy from tears
Researchers at the University of Utah have developed a new power source for smart contact lenses, combining a flexible silicon solar cell with a device that generates energy from tears, enabling the self-sufficient operation of these lenses. This innovative hybrid unit provides a practical solution to the challenge of powering eye-based technologies, eliminating the need for external batteries or cumbersome wireless power transfer. The device’s ability to continuously harvest energy through natural light and the electrolytes in tears holds promise for a range of applications, from health monitoring to augmented reality experiences, directly within the eye’s environment (IEEE Spectrum).
5. Mini-liver
LyGenesis has initiated a clinical trial where healthy liver cells are injected into a patient’s lymph node to form a “mini liver,” potentially offering an innovative solution for individuals with liver failure who are ineligible for transplants. This approach, which has shown promise in animal models, could utilize lymph nodes as sites for generating functional liver tissue, aiming to alleviate the shortage of donor organs and provide an interim solution for patients with end-stage liver disease (Nature).
Articles
1. The race to fix space-weather forecasting before next big solar storm hits (MIT Technology Review)
As solar activity increases with the new solar cycle, scientists are racing to improve space-weather forecasting to prevent potential collisions caused by atmospheric changes affecting satellite trajectories. The recent incident where a solar storm impacted SpaceX’s Starlink satellites has catalyzed efforts to enhance models that predict atmospheric density changes, vital for satellite navigation and safety in space. This endeavor is crucial as the number of satellites grows exponentially, making accurate space-weather predictions essential to avoid catastrophic orbital debris collisions and ensure the safety of space operations.
2. Philip Tetlock on teaming up with AI (Financial Times)
Philip Tetlock is a renowned social scientist known for his work on expert judgment and forecasting. He believes AI and humans can collaborate effectively, with AI potentially able to synthesize different schools of thought better than humans and become a form of “superintelligence.” Tetlock sees AI-human collaboration, particularly in developing systems that can capture different viewpoints and combine them optimally, as a key frontier for the next 30 years.
3. The human side of generative AI: Creating a path to productivity (McKinsey)
The adoption of generative AI (gen AI) in the workplace is expanding rapidly, impacting a wide array of roles beyond just technical positions, with 88% of employees in a McKinsey survey using gen AI for non-technical tasks. Despite the potential productivity gains, 51% of gen AI users and creators are considering leaving their jobs, prioritizing factors like workplace flexibility, meaningful work, and supportive leadership over compensation. As gen AI continues to evolve, it’s crucial for organizations to focus on human-centric job designs, enhancing cognitive and social-emotional skills, and maintaining a dialogue with employees to navigate the integration of gen AI effectively and sustain employee engagement and productivity.