Courtesy
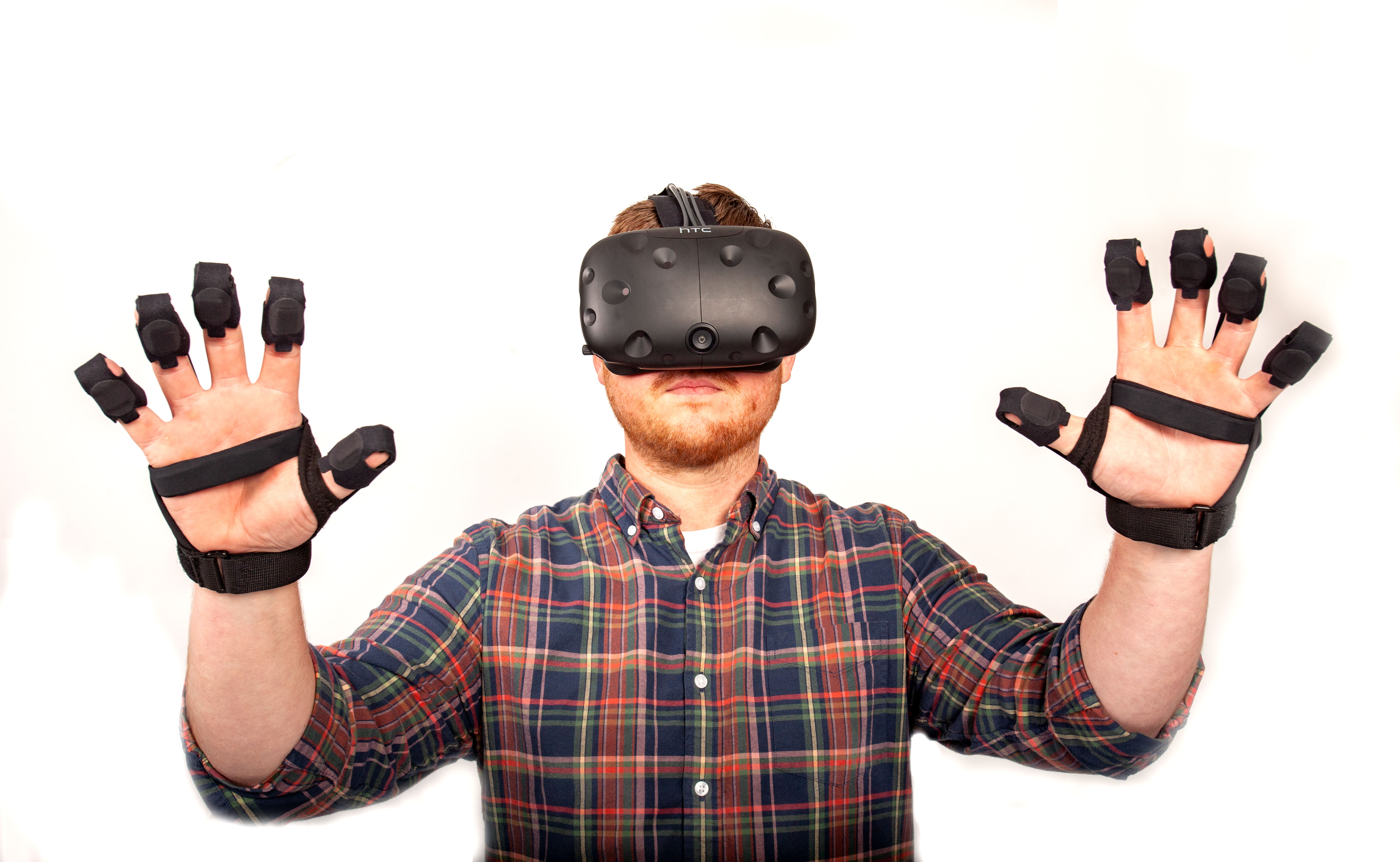
BeBop sensors is a company that produces fabric material-based sensors that turn pressure, twist, bend and stretch into electric signals. The sensor has application in healthcare, gaming and automotive industries. In healthcare, for example, the sensor is put into hospital beds, wheelchairs and shoe insoles to detect pressure points. One of the most interesting applications is its Forte wireless gloves. The gloves are essentially digital hands and enable the manipulation of objects in virtual reality (VR). The gloves are one-size-fits-all and can function for more than 15 hours wirelessly. This invention is important because virtual reality had decent visual and audio effects but no touch. The sensors in the gloves are sensitive and accurate so that people can see precisely where hands and fingers are in VR games. In addition, it can generate the sensation of touching something in a VR environment. For example, in a demo of watering plants in VR, people are able to get a sense of water rushing out of the can. In short, virtual reality is getting closer to reality.
It might be interesting to use this technology for exploring a space virtually, such as a VR demo of a house or a museum, either as marketing or as entertainment. VR-based hands-on 4-D movies might become popular.
It might be of scientific value to study how the gloves-generated signals relate to brainwave or neural activities. The gloves might be used to play virtual music instruments, train surgeons, athletes and other hands-on professions. If the sensitivity is high enough, this sensor will essentially turn touch into data, adding to a whole new set of big data. For example, putting the sensors into a soccer star’s socks (or maybe a soccer ball) may help us understand why the athlete is exceptional in certain moves, touches or techniques. Eventually, we may actually be able to produce soccer-playing robots.
The gloves’ technology might also be used as a new way of operating computers (or TV and other appliances). The keyboard might be projected onto a flat surface. Or, there could be a 3 dimensional keyboard and new way of interaction, such as manipulating 3-D maps or virtual human body. Cell phone might be replaced with a small watch that can project 3-D images.
What if clothes are made of this technology? Maybe a more immersive VR is possible such that the whole body can feel the virtual reality.
Link: https://bebopsensors.com/
Contact: webpage
Location: California, US
Mentioned: among the best inventions of the year by Time
Purpose
Enrich VR (such as with hand operations and the sense of touch)
Idea
Converts senses and electric signals into each other (such as using gloves made of a special material)
Further Possibilities
1. Use the Forte gloves to play virtual sports, virtual musical instruments or train surgeons.
2. Put the sensors into sporting equipment to learn how athletes perform. Use the data to train people or sports-playing robots
3. Use the gloves’ technology to build a new human-computer interface, such as 3-D keyboard or 3-D interactive maps.
4. An immersive VR with sensor-based clothes
5. Use the glove-derived data to train robotic hands in handling delicate objects
Questions
1. How might we make VR more realistic?
2. How else might we use the sense of touch in the digital world?
3. How might we experience others’ life through VR?